Behavioural changes under COVID-19 in Hong Kong

In response to our research questions, we have conducted a review of the secondary literature - The “Catalogue of New Habits and Value Concepts” is a compilation of values and behaviour changes observed among the public and institutions within Hong Kong during the COVID-19 pandemic, corresponding with certain targets and sub-targets under the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs).
This Catalogue was developed as a part of the research - conducted by the HKUST Division of Environment and Sustainability (ENVR), supported by the Robert H.N. Ho Family Foundation Hong Kong - that seeks to understand what has changed among Hong Kongers during the pandemic, and what the implications of these changes are to sustainable development and recovery. These changes are ranked in order of their relevance to the COVID-19 situation of Hong Kong, and the rankings were determined by the researchers based on existing documentation of experiences and policies in Hong Kong – from news reports, social media, government mandates and programs, among others. This Catalogue provides baseline data for our work to compile habit-driven behavioural patterns related to the achievement of relevant SDG key indicators, and is useful for us to (1) prepare a deliberation guide/briefing material and (2) design a public opinion survey instrument.
In the top 15 of 75 final rankings, four SDGs, in particular, stand out: SDG 3 (Good Health and Wellbeing), SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), SDG 1 (No Poverty), and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities). These trending SDGs are reflective of the impacts the pandemic has had on human health, the local and global economies, as well as the disproportionate impacts on vulnerable and discriminated communities. Below are the key observations (the "new normals") for our reflection and further investigation.
10 Quick Facts - Changes among Hong Kongers during the pandemic

1. Increased hygiene behavior and associated waste production
Relevant Sustainability Goal: #3
Stringent health protocols have required the use of masks in all public places since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak in 2020. In addition, many people have reported that it has become not only a habit but also a necessity to constantly disinfect – one’s hands, belongings, surfaces and places used, among others.
The production of waste generated due to COVID-19 pandemic is massive (e.g., single-use masks and other personal/public sanitizing agents). The management of these new waste problems needs to be seriously considered with new measures factored in in the existing waste management policy.
 Source: Tatler
Source: Tatler

2. Increased takeaway orders with disposable cutlery and plastic bags
Relevant Sustainability Goals: #8, #11, #12
More than 100 million pieces of disposable cutlery and plastic bags are disposed of every week in Hong Kong, as the number of takeaways and food deliveries have increased as people practice social distancing in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. How could we seize this opportunity to promote BYOB practice and the use of sustainable utensils?
 Source: HKFP
Source: HKFP

3. Decreased traveling abroad for leisure
Relevant Sustainability Goal: #3
Traveling abroad for leisure has taken a steep decline in the last 1.5 years, especially with Hong Kong’s very stringent quarantine protocols upon return. The near-total collapse of travel has led to plummeting from 2019’s 55.9 million to just 3.57 million arrivals in 2020 amid coronavirus pandemic – 36-year low for tourism hub. This hard hit has massively altered the tourism-related ecosystem and at the same time shifted the capital to savings and other expenditures.


4. Decreased private consumption
Relevant Sustainability Goal: #8
People in Hong Kong reduced their private consumption during COVID to keep savings. Especially in 2020, when many were working or learning from home and many public establishments were closed, people did not see the need to go shopping for non-essential items since they were just at home most of the time. With the global economy also in a recession due to the pandemic halting many industries (e.g. hospitality, travel, dining), people tried to save more to prepare for uncertainties related to their jobs.
 Source: SCMP
Source: SCMP

5. Increased plastic use
Relevant Sustainability Goals: #12, #18
Plastic use in Hong Kong increased by 50 per cent when dining in restaurants was banned all day. However, put recycling aside, some restaurants try to eliminate plastic waste by finding eco-friendlier alternative materials, e.g. compostable cups and utensils. Most stores are now opting for a greener options, such as not giving away straws, discounts for bringing own reusable cups and bags, etc.

6. Low interest in online learning
Relevant Sustainability Goal: #4
During the period when face-to-face classes were not allowed, students generally expressed a below average experience with online learning and low learning satisfaction. In addition, underprivileged students do not even have the available technologies (e.g. computers, tablets, or fast Wi-Fi) to fully follow online classes. Under the online schooling policy, 90% of teachers have also reported that they are falling behind schedule.

7. Increased household burdens and stress
Relevant Sustainability Goals: #10, #4
Under COVID-19, the household responsibilities have greatly increased due to school suspension, and women are often expected to handle this extra pressure with their ongoing jobs. In addition, domestic helpers have reported being very overworked especially during the period where families were working and learning from home.
 Source: SCMP
Source: SCMP

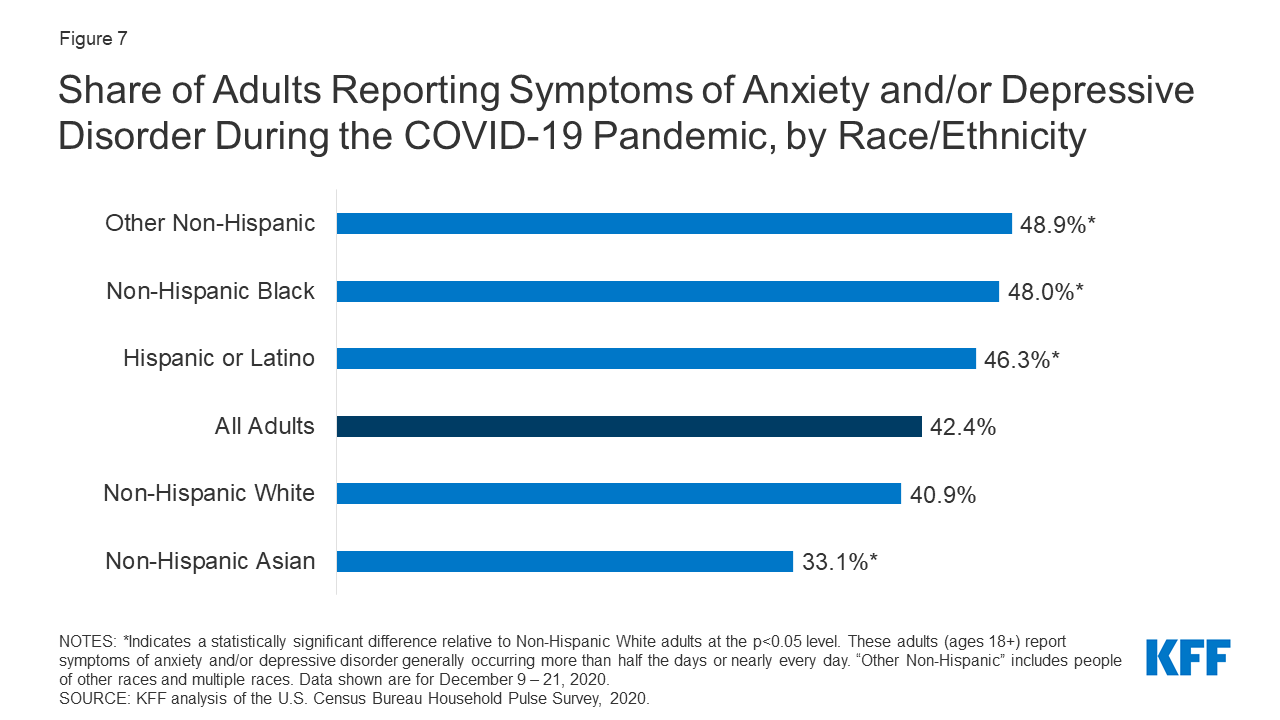
8. Increased anxiety and depression
Relevant Sustainability Goals: #3
Compared with 2016 and 2017, the population stress level, prevalence of anxiety, and the depression symptoms drastically increased during the COVID-19 outbreak. This could be related to the necessary social distancing and isolation measures to prevent the spread of the virus. In addition, with the closing down of many public places, prohibition of large gatherings, and difficulty to travel abroad, people may have felt very lonely and detached from their friends and family.
 Source: KFF
Source: KFF

9. Increased online business
Relevant Sustainability Goal: #8
Local Hong Kong businesses sustain their business online: even if the brick and mortar stores are closed, many online sites are still up and running (e.g., Mannings, Watsons, Nike - retail shops also changed to online platforms). Reorientations of business models as everything from commerce to events move online and major corporations are forced to reengineer supply chains, ecosystems, processes, products, and technology strategies to meet the requirements of a new global market.
On the consumer side, people have reported increased online buying during the pandemic as it is more convenient, and many discounts and promotions were available through online shopping vs. physical shopping.
 Source: SCMP
Source: SCMP


 Source:
Source: